Types Of Network Analysis in ArcGIS
What is Network Analysis in ArcGIS ?
ArcGIS Network analysis provides network-based spatial analysis tools for solving complex routing problems. It uses a configurable transportation network data model allowing organizations to accurately represent their unique network requirements.
Types of Network Analysis
Route:
What is the best route?
Regardless
of whether tracking down a basic course between two areas or one that visits a
few areas, individuals normally attempt to take the best course. In any case,
"best course" can mean various things in various circumstances.
All
that course can be the speediest, briefest, or most panoramic detour,
contingent upon the impedance picked. Assuming the impedance is time, the best
course is the speediest course. Consequently, all that course can be
characterized as the course that has the least impedance, where the impedance
is picked by the client. Any legitimate organization cost trait can be utilized
as the impedance while deciding the best course.
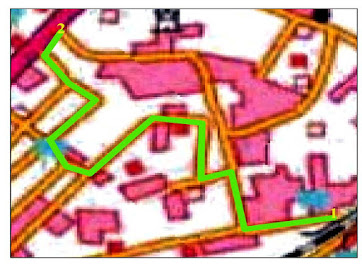
In
the model beneath, the main case utilizes time as an impedance. The fastest way
is appeared in blue and has an all out length of 4.5 miles, which requires 8
minutes to navigate.
In the following case, distance is picked as the impedance. Subsequently, the length of the briefest way is 4.4 miles, which requires 9 minutes to cross.
Alongside the best course, Network Analyst furnishes headings with turn-by-turn maps that can be printed.
Service areas:
Closest facility:
Tracking down the nearest emergency clinic to a mishap, the nearest squad cars to a crime location, and the nearest store to a client's location are altogether instances of nearest office issues. When discovering nearest offices, you can indicate the number of to discover and whether the course of movement is toward or away from them. Whenever you've tracked down the nearest offices, you can show the best course to or from them, return the movement cost for each course, and show bearings to every office. Also, you can indicate an impedance cutoff past which Network Analyst ought not look for an office. For example, you can set up a nearest office issue to look for emergency clinics inside 15 minutes' drive season of the site of a mishap. Any clinics that take longer than 15 minutes to arrive won't be remembered for the outcomes.
OD cost matrix:
The straight lines can be represented differently, for example, by shading, addressing which point they begin from, or by thickness, addressing the movement season of every way.
The straight lines can be represented differently, for example, by shading, addressing which point they begin from, or by thickness, addressing the movement season of every way.
Vehicle routing problem
A dispatcher dealing with an armada of vehicles is frequently needed to settle on choices about vehicle directing. One such choice includes how to best allot a gathering of clients to an armada of vehicles and to arrangement and timetable their visits. The targets in taking care of such vehicle directing issues (VRP) are to give a significant degree of client support by regarding any time windows while keeping the generally speaking working and speculation costs for each course as low as could really be expected. The requirements are to finished the courses with accessible assets and inside as far as possible forced by driver work shifts, driving paces, and client responsibilities.
Consider an illustration of conveying products to supermarkets from a focal distribution center area. An armada of three trucks is accessible at the distribution center. The stockroom works just inside a specific time window-from 8:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m.- during which all trucks should return back to the distribution center. Each truck has a limit of 15,000 pounds, which restricts the measure of merchandise it can convey. Each store has an interest for a particular measure of merchandise (in pounds) that should be conveyed, and each store has time windows that limit when conveyances ought to be made. Moreover, the driver can work just eight hours of the day, requires a break for lunch, and is paid for the sum spent on driving and overhauling the stores. The objective is to thought of an agenda for every driver (or course) with the end goal that the conveyances can be made while respecting all the assistance prerequisites and limiting the all out time spent on a specific course by the driver. The figure beneath shows three courses got by tackling the above vehicle steering issue.
Location - allocation
1) Given a bunch of existing fire stations, which site for another fire station would give the best reaction times to the local area?
2) On the off chance that a retail organization needs to cut back, which stores would it be advisable for it to near keep up the most in general interest?
3) Where should a processing plant be worked to limit the distance to circulation focuses?
In
these models, offices would address the fire stations, retail locations, and
production lines; request focuses would address structures, clients, and
dispersion focuses.
The goal might be to limit the general distance between request focuses and offices, amplify the quantity of interest focuses covered inside a specific distance of offices, augment an allocated measure of interest that rots with expanding distance from an office, or boost the measure of interest caught in a climate of cordial and contending offices.
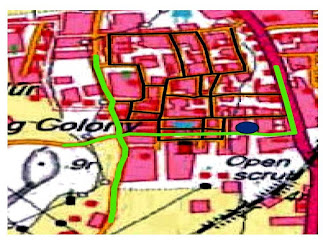
The guide underneath shows the consequences of an area designation examination intended to figure out which fire stations are repetitive. The accompanying data was given to the solver: a variety of fire stations (offices), road midpoints (request focuses), and a greatest suitable reaction time. The reaction time is the time it takes firemen to arrive at a given area. The area designation solver discovered that the local group of fire-fighters can close a few fire stations and still keep a three-minute reaction time.
A guide of 16 fire stations: the seven that are needed to stay open to cover request focuses inside three minutes, and the nine that could close.
Out of the current arrangement of fire stations, nine fire stations can close, and at least seven are required for the office to in any case have the option to react to crises inside three minutes.
Time dependent analysis
The
entirety of the solvers recorded above permit you to consolidate live and
verifiable traffic information into an investigation so you can track down the
best course for a given time frame of day; find the best spot to relational
word an emergency vehicle at 8:00 a.m., 12:00 p.m., 4:00 p.m, etc; and create
administration regions for various times. The aftereffects of any examination
may change for various dates and times since traffic conditions and travel
times may change.